Mesothelioma Types by Location
There are four types of mesothelioma defined by the location in which they develop.
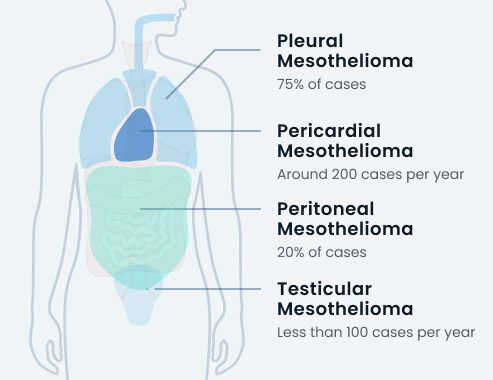
The Four Types of Mesothelioma
- Pleural mesothelioma develops in the lining of the lungs
- Peritoneal mesothelioma develops in the abdominal lining
- Pericardial mesothelioma develops in the heart lining
- Testicular mesothelioma develops in the lining of the testes
A patient’s prognosis and life expectancy are significantly influenced by the type of mesothelioma they are facing. The average life expectancy of patients with pleural or pericardial mesothelioma is six months to a year. About half of peritoneal and testicular mesothelioma patients live at least five years after surgery.
-
Pleural Mesothelioma (Lungs)
About 75% of mesothelioma cases develop in the pleural lining of the lungs. Primary symptoms include chest pain, difficulty breathing, dry cough, weight loss, fever and fatigue. Life expectancy without treatment is around eight months. Chemotherapy helps patients live around one year and those who qualify for surgery often live several years. A new therapy called Tumor Treating Fields is being combined with chemotherapy to improve survival by an additional six months. -

Peritoneal Mesothelioma (Abdomen)
Approximately 20% of cases develop in the peritoneal lining of the abdomen. Primary symptoms include abdominal pain, bloating, bowel changes, loss of appetite and weight loss. Life expectancy without treatment is around six months. Chemotherapy helps patients live around one year with the disease. Just over half of those who qualify for aggressive surgery with heated chemotherapy live longer than five years. -

Pericardial Mesothelioma (Heart)
Less than 1% of cases develop in the pericardial lining of the heart. Symptoms include heart palpitations and murmurs, chest pain, difficulty breathing, fatigue and fever. Life expectancy is around six months with or without treatment. Some patients have lived for several years after undergoing surgery. -
Testicular Mesothelioma
Less than 1% of cases develop in the lining of the testes. Symptoms of testicular mesothelioma include swelling of the scrotum, testicular pain, scrotal lumps or fluid in the scrotum. About half of patients have a life expectancy of around five years. Nearly a third of patients live 10 years. The most common treatments include surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy.

Benign vs. Malignant Mesothelioma
Not all cases of mesothelioma are considered malignant or cancerous. Cases of benign or noncancerous mesothelioma occur, and they are easier to treat and control. It is extremely rare; only several hundred cases have been described in medical literature.
Unlike malignant mesothelioma, the benign form of the disease responds well to treatment and rarely recurs after surgery. In the rare cases that have recurred, most come back benign and respond well to another surgery.
Some cases of benign mesothelioma have recurred as a malignant form of the disease. It is extremely rare, but it causes doctors to closely monitor benign mesothelioma patients for new tumors.
Mesothelioma Cell Types
Mesothelioma occurs as one of three types of cancer cells: Epithelioid, sarcomatoid or biphasic, which is a combination of both. Determining the mesothelioma cell type helps the doctor design the most effective treatment plan for each patient.
Histology is the medical term for the microscopic study of these cells, and it involves immunohistochemistry tests to accurately identify cells. An accurate mesothelioma diagnosis is important because it helps your doctor determine the best treatment option and provide an assessment of your life expectancy.
-
Epithelioid Mesothelioma
Epithelioid mesothelioma cells are square shaped with visible nuclei, and they tend to lump together. They are the most common type of cancerous mesothelioma cell, accounting for 50% to 70% of all mesothelioma cancers. Because they are the most treatable cell type, patients with epithelial cells have the most favorable prognosis. -

Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma
Sarcomatoid mesothelioma cells appear spindle shaped with plump, elongated nuclei. They generally overlap one another. This cellular pattern is seen in about 10% to 20% of all mesothelioma tumors. Because they are the most aggressive cells, there are fewer treatment options for patients with this cell type. -
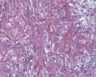
Biphasic Mesothelioma
Biphasic mesothelioma cells are a mixture of epithelial and sarcomatoid cells. Approximately 20% to 35% of all mesothelioma tumors are biphasic. Prognosis varies depending on the mixture of cells, and is more favorable in cases that contain more epithelial cells than sarcomatoid cells. If the tumor contains mostly sarcomatoid cells the cancer is likely to be more aggressive.
Rare Mesothelioma Cell Types
- Adenomatoid cells, which may be benign
- Cystic cells, which are more common in peritoneal mesothelioma cases
- Desmoplastic cells, which are more common in pleural mesothelioma cases
- Small cells, which occur more commonly in the abdomen
- Well-differentiated papillary cells, which are associated with a better prognosis
Treatment by Mesothelioma Type
The type of mesothelioma you are diagnosed with will impact your treatment plan. The treatments your doctor recommends will depend on the stage of mesothelioma, the location of your cancer and the cell type.
Pleural Mesothelioma Treatment Options
The two aggressive surgical procedures available for pleural mesothelioma include extrapleural pneumonectomy and pleurectomy and decortication. The latter spares the lung. Both surgeries may extend survival by years.
The most effective chemotherapy drugs against pleural mesothelioma include cisplatin and pemetrexed (Alimta).
Radiation therapy is successful for pleural mesothelioma when used alone or in combination with surgery.
Mesothelioma clinical trials offer access to new innovative therapies such as immunotherapy, photodynamic therapy and gene therapy. There are more clinical trials for the pleural type because it is far more common than the other types of mesothelioma.
Palliative care is widely used in mesothelioma treatment to control pain and relieve the symptoms of mesothelioma.
Peritoneal Mesothelioma Treatment Options
Surgery for peritoneal tumors is known as a peritonectomy, and it is usually combined with heated chemotherapy. A pericardiectomy removes pericardial tumors, and an inguinal orchiectomy removes testicular tumors.
The chemotherapy drugs that work best for peritoneal mesothelioma include gemcitabine, Alimta, mitomycin and carboplatin.
Radiation therapy isn’t used for peritoneal mesothelioma because of the potential damage to abdominal organs.
Palliative care options for peritoneal patients include paracentesis to drain fluid from the abdomen, physical therapy and medication to control pain, inflammation and digestive issues.
Peritoneal mesothelioma clinical trials are underway throughout the U.S. testing new drugs and surgical techniques.
Pericardial and Testicular Mesothelioma Treatment Options
No chemotherapy combination is officially accepted for these two types of mesothelioma because they are so rare. Doctors decide which chemotherapy drugs to use based on their experience and the individual patient’s health.
Radiation therapy is considered successful in the treatment of both pericardial and testicular mesothelioma.
These types of mesothelioma are so rare that clinical trials are not feasible, but some trials have accepted testicular mesothelioma patients.
Patients are encouraged to communicate their needs and concerns to their health care team. Treatments are available to manage all types of mesothelioma, and working with an expert who specializes in your specific type of mesothelioma could make all the difference.



