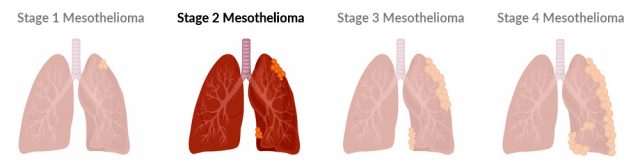
Stage 2 Mesothelioma
Stage 2 pleural mesothelioma indicates cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes. Metastasis is possible, but prognosis is still favorable, and surgery remains an option. About 38% of patients diagnosed with stage 2 pleural mesothelioma survive for at least two years.
What Is Stage 2 Mesothelioma?
Stage 2 mesothelioma is marked by the advancement of cancer cells into the hilar lymph nodes.
The hilar lymph nodes are located roughly midway down and toward the back of the lungs, where arteries, veins and nerves form the root of the lungs.
Stage 2 tumors also have developed in the mesothelium, the membrane lining that surrounds the chest cavity and lungs. Cancer may also have infiltrated the diaphragm muscle, located under the lungs, which works to expand the thoracic cavity during breathing.
Pleural mesothelioma has not yet spread to distant tissues and organs, and the prognosis is better than in later stages.
Peritoneal mesothelioma develops in the lining of the abdomen but does not have a formal staging system.
Characteristics of Stage 2 Mesothelioma
The staging method most often used to define the stages of mesothelioma and other cancers is the TNM classification system.
At stage 2, cancer has grown into the pleural lining of one side of the chest wall and may have advanced into the lung itself. It’s also possible that tumor growth has occurred in the diaphragm, the muscle which expands the chest cavity for breathing.
Stage 2 pleural mesothelioma is also characterized by the spread of cancer to lymph nodes on the same side of the body as the main tumor. In this stage, cancer has not yet metastasized to distant sites within the body.
Researchers are working to develop a formal staging system for peritoneal mesothelioma, but the disease is sometimes considered stage 2 if there is local tumor growth with some lymph node involvement.
Stage 2 Mesothelioma Causes
Mesothelioma is almost exclusively caused by asbestos. Asbestos fibers are microscopic, barb-shaped particles, which can easily be released from many asbestos-containing materials.
Inhaling or digesting these sharp fibers traps them in the lining of the lungs or other areas of the body.
These fibers trigger an immune response that causes inflammation and scarring in the tissue over long periods.
Chronic inflammation as a result of the asbestos fibers causes damage to cells and DNA, leading to improper cellular replication and the formation of tumors.
Symptoms of Stage 2 Mesothelioma
Similar to stage 1, there are usually no major mesothelioma symptoms in stage 2. When present, these symptoms may be broad and mimic many other diseases.
Signs of Stage 2 Mesothelioma
- Persistent cough
- Nausea, fatigue or weight loss
- Minor chest pain
- Slight difficulty breathing
- Insomnia
- Fever
Doctors and patients commonly mistake these symptoms for the flu, pneumonia or bronchitis.
As tumors develop, fluid accumulates between the layers of the pleura and causes excess pressure on the lungs. This is known as pleural effusion and leads to dyspnea or increased difficulty breathing.
Pleural effusion may occur during this stage, though it is more common in stage 3 and stage 4 mesothelioma.
The symptoms for pleural and peritoneal mesothelioma may overlap during this stage, making diagnosis more difficult in the early stages.
More advanced peritoneal mesothelioma may present with gastrointestinal distress, and late-stage pericardial mesothelioma typically causes irregular heart rhythms.
Stage 2 Mesothelioma Prognosis
A mesothelioma diagnosis at this stage has a two-year survival rate of 38%. Surgery is still appropriate as a treatment because the tumors remain largely consolidated.
Aggressive treatment is more available, and a wider range of therapies are afforded in early-stage mesothelioma. About 11% of patients diagnosed in stage 2 have a mesothelioma life expectancy of five years or more.
The survival rate decreases for later stages of the disease. For comparison, roughly 7% of patients diagnosed with stage 4 mesothelioma will survive for five years and the average life expectancy is around one year.
However, treatments continue to improve over time, and survival rate statistics may not reflect the most current outcomes in mesothelioma care.
Cancer cell type and overall health ultimately determine diagnosis and treatment for stage 2 mesothelioma. A patient in better health will have access to more aggressive treatment options.
Epithelioid cell type is easier to surgically remove, and patients have a better survival prognosis with a longer life expectancy. Roughly 60% of mesothelioma cases are epithelioid.
Fibrous sarcomatoid and biphasic (mixed) cell types are more aggressive forms of cancer that do not often respond as well to treatment. These cases comprise about 40% of all mesothelioma patients.
Is There a Cure for Stage 2 Mesothelioma?
There is currently no cure for any stage of mesothelioma. Many mesothelioma treatments aim to shrink tumors, prevent cancer growth or decrease the severity of symptoms.
Remission is the absence of new tumor growth and possible with treatment during this stage. There is a greater chance of remission if mesothelioma is treated during stage 2, and surgery is the best treatment option at this stage.
Some mesothelioma survivors have undergone new therapies through clinical research trials and improved their life expectancy by several years.
Treatment Options for Stage 2 Mesothelioma
Surgery
The most common and effective surgical options for stage 2 pleural mesothelioma are extrapleural pneumonectomy and pleurectomy with decortication. Treatment plans will depend on how far cancer has spread.
Extrapleural pneumonectomy is an aggressive surgery that removes the entire affected lung, linings of the heart and lungs, affected lymph nodes and a portion of the diaphragm.
Pleurectomy and decortication is a less aggressive alternative that removes the pleural lining of the lungs along with any visible tumors. The surface of the lung is then scraped to remove the remaining cancer cells, and the lung is not removed.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy is often used in combination with surgery to treat stage 2 mesothelioma but may be prescribed on its own.
Pemetrexed (Alimta) is used in combination with cisplatin as the most effective first-line treatment for mesothelioma.
Delivery of chemotherapy can occur before, during or after surgery.
The hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy (HIPEC) procedure is one of the best options for stage 2 mesothelioma. This method involves washing the abdominal cavity with a heated chemotherapy solution for 60 to 90 minutes immediately after surgery.
Radiation
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to kill cancer cells in a specific and discrete location while minimizing damage to neighboring healthy tissue.
Radiotherapy is often used to alleviate pain and other symptoms of tumors that have caused excess pressure on the lungs or other organs.
Clinical Trials
Patients with stage 2 mesothelioma often qualify for clinical research trials due to their lack of severe symptoms.
These studies allow patients the opportunity for otherwise unavailable and potentially effective therapies such as immunotherapy, gene therapy and new chemotherapy options.
Living with Stage 2 Mesothelioma
Patients have options when it comes to improving their mesothelioma prognosis and quality of life.
Lifestyle changes, such as improved diet and exercise, can increase overall health and prolong survival. Many patients seek help from support groups and loved ones. Support networks provide motivation and help patients advocate for their care.
Stage 2 mesothelioma is highly treatable, and patients at this stage typically respond well to chemotherapy, surgery and radiation.


