Sarcomatoid cell mesothelioma tends to be more aggressive and more resistant to cancer therapy compared with other mesothelioma cell types.
These tumors also are referred to as sarcomatous, spindled or diffuse malignant fibrous mesothelioma.
What Do Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma Cells and Tumors Look Like?
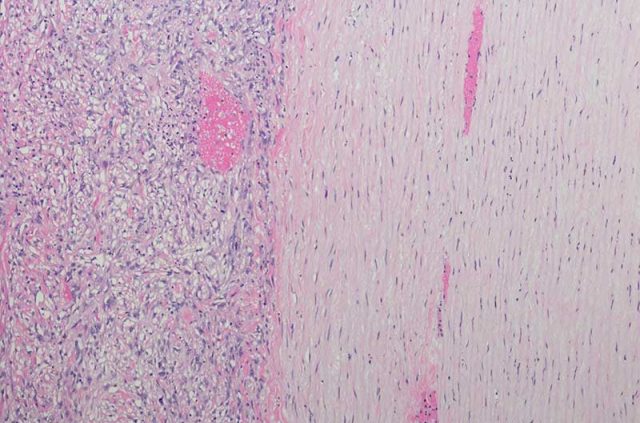
Sarcomatoid cells are one of three designations for mesothelioma cells. They are spindle shaped and have an overlapping appearance within a tumor.
As they form tumors, sarcomatoid cells most often appear as small nodules or groupings scattered across the surface of the pleura — the thin membranes lining the chest cavity and surrounding the lungs.
The nodules can merge to form a sheet-like tumor on the lining around the lungs. Because the tumors tend to spread out over a larger area, they can be difficult to treat effectively.
In rare cases, a single sarcomatoid mesothelioma tumor mass may form. This also can be challenging to treat. Sometimes the tumor has grown into the chest wall and it cannot be removed surgically.
What Are the Symptoms of Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma?
According to a 2019 Expert Review of Respiratory Medicine article, nonspecific symptoms of pleural mesothelioma can include cough, shortness of breath, chest wall pain, weight loss and fatigue.
Symptoms tend to be similar regardless of the mesothelioma cell type.
Many less serious diseases share these signs. This makes diagnosing pleural mesothelioma challenging, because the cancer is easily mistaken for asthma, bronchitis or pneumonia.
When a patient visits their doctor with complaints of shortness of breath or persistent cough, they may be treated with an inhaler or antibiotics first.
Mesothelioma is rare, and many primary care physicians will not consider it.
When things worsen or do not improve, the doctor may refer the patient to a pulmonologist for additional lung tests or physical exams.
Pleural effusion — the accumulation of fluids around the lungs — tends to be less common with sarcomatoid mesothelioma compared with other forms of the disease. If it does occur, it is typically accompanied by shortness of breath and chest pain.
Because sarcomatoid tumors can grow into the chest wall, some patients experience significant chest pain.
Other potential pleural mesothelioma symptoms include wheezing, fever or night sweats, muscle weakness, loss of appetite and trouble swallowing.
Why Is the Sarcomatoid Cell Type Difficult to Diagnose?
Because symptoms are nonspecific, diagnosing any type of mesothelioma can be challenging.
Sarcomatoid mesothelioma presents additional difficulties, because the tumors can resemble benign (noncancerous) conditions or other types of cancer.
Under a microscope, sarcomatoid tissue samples can appear similar to sarcoma, fibrosarcoma, fibrous pleurisy, malignant fibrous histiocytoma, localized fibrous tumors, pleural liposarcoma or metastatic renal cell carcinoma.

How Is Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma Diagnosed?
Diagnosis typically starts with imaging studies such as X-rays, a CT scan or an MRI. These tests cannot confirm mesothelioma but can reveal abnormalities in the lungs.
If cancer is suspected, a surgeon can review the imaging studies and make a plan to obtain a biopsy or multiple biopsies (tissue samples) of the tumor.
For patients with widespread pleural mesothelioma or multiple tumors, removing the entire tumor may not be an option. This makes the biopsy the most important diagnostic tool.
Surgeons often obtain biopsy samples using thoroscopy or video-assisted thoracic surgery procedures, which allows the surgeon to view the tumor during sampling. This increases the chances of an accurate sarcomatoid cell mesothelioma diagnosis.
If you suspect you may have an asbestos-related disease, seek out a mesothelioma specialty cancer care team. This group is more likely to include a pathologist who is familiar with the disease and the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2018 pleural mesothelioma treatment guidelines.
This is important because the guidelines provide pathology testing recommendations.
Why Is Accurate Sarcomatoid Cell Type Diagnosis Important?
If you want to participate in a pleural mesothelioma clinical trial, your oncologist needs to know as much about your tumor as possible.
Your medical team can use these details to help you find a clinical trial to best match your needs and type of mesothelioma.
In a 2019 study published in Pathology International, researchers described an example of how this detailed cell information may help patients. The authors identified details about one patient’s epithelial mesothelioma tumor.
They found specific call markers indicating the cancer was susceptible to newer immunotherapy drugs. Without the detailed pathology report, oncologists wouldn’t know this is a possibility.
Sarcomatoid is the most aggressive cell type of mesothelioma. Access to newer, cutting-edge therapies can be an important part of improving length and quality of life.
How Does a Sarcomatoid Diagnosis Affect Treatment?
Most patients are treated based on the stage of mesothelioma and tumor location, but sarcomatoid cancer can be more aggressive than other types.
Obtaining an accurate sarcomatoid diagnosis provides important information to your medical team for planning treatment.
While some pleural mesothelioma tumors can be removed with surgery, the structure and extent of sarcomatoid tumors sometimes makes surgery impossible.
However, this doesn’t mean you can’t get other life-extending mesothelioma treatments. A combination of chemotherapy and radiation therapy may be used in an approach called multimodal therapy.
Clinical trials for sarcomatoid mesothelioma also are an option. Seeking care from a specialized mesothelioma program can improve treatment options and resources for patients as well.


