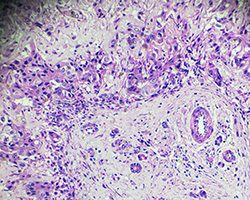
Epithelial cell pleural mesothelioma — sometimes called epithelioid mesothelioma — affects the pleura, the membranes lining the chest cavity and surrounding the lungs.
These cells are shaped like cubes and are more responsive to treatment than biphasic cells and sarcomatoid cells.
Visually, epithelioid cells appear different from other mesothelioma cells because they tend to clump together.
Between half and 70 percent of all mesothelioma cancers are epithelioid, making it the most common mesothelioma cell type found in these tumors.
Most cancer cells are assigned a type based on the tissue they arise from. The epithelial cell type forms on normal epithelial tissue.
What Are the Symptoms of Epithelial Mesothelioma?
The symptoms of pleural mesothelioma tend to be similar regardless of the tumor cell type. Authors of a 2019 Expert Review of Respiratory Medicine article describe early pleural mesothelioma symptoms as nonspecific.
These symptoms of mesothelioma, such as cough, shortness of breath, chest wall pain, weight loss and fatigue, make diagnosing pleural mesothelioma challenging.
Patients often visit their primary care physician first with complaints of shortness of breath or persistent cough. Because mesothelioma is rare, many doctors will not consider mesothelioma as a potential cause of symptoms.
Referral to a pulmonologist to investigate symptoms often occurs before an oncologist is consulted.
How Does a Doctor Diagnose Epithelial Mesothelioma?
Receiving an accurate epithelial pleural mesothelioma diagnosis isn’t easy. Most symptoms mimic signs of less severe respiratory conditions such as asthma or pneumonia. This can lead to misdiagnosis early in the diagnostic process.
After a doctor has ruled out more common causes of a patient’s symptoms, they may refer the person for imaging tests such as X-rays, a CT scan or an MRI.
These tests cannot diagnose mesothelioma. However, they can reveal abnormalities in the lungs. This will alert the doctor to the potential for cancer. Images also provide important information on the location of possible tumors.
Once cancer is being considered, the patient will be referred to a surgeon to obtain a biopsy or multiple biopsies of the tumor.
Surgeons often obtain biopsy samples using thoroscopy or video-assisted thoracic surgery procedures, which allows the doctor to see the tissue while sampling it. This increases the chances of an accurate epithelial cell pleural mesothelioma diagnosis.
If complete tumors are removed during surgery, this also can provide an accurate diagnosis. If more than one cell type is present, having the entire tumor to examine will increase the chances of finding the different cells.
Confirming an Epithelial Diagnosis
Histology lab tests — including tissue typing and biomarker identification — can help confirm an accurate mesothelioma diagnosis.
The ASCO 2018 pleural mesothelioma treatment guidelines recommend immunohistochemistry for testing suspected mesothelioma tumors. This specialized lab examination of cells can confirm the absence and presence of mesothelioma cell markers.

What Are the Pleural Mesothelioma Epithelial Cell Subtypes?
There are more than a dozen epithelial cell subtypes. Doctors do not know exactly what percent of patients are diagnosed with each cell subtype.
It can be helpful for your doctors to understand which epithelial subtype make up your cancer.
If you want to participate in a pleural mesothelioma clinical trial, knowing as much about your tumor as possible will help your medical team determine which clinical trial may be a good match for you.
For example, a 2019 study published in Pathology International identified a patient with a unique histiocytoid tumor that appeared to be a good candidate for treatment with newer immunotherapy drugs.
This type of information may help a patient gain access to newer, cutting-edge therapies.
Subtypes of Epithelial Mesothelioma
- Deciduoid
- Diffuse — Not otherwise specified (NOS)
- Tubulopapillary
- Glomeruloid
- Glandular
- Small cell
- Histiocytoid
- Poorly differentiated
- Adenoid cystic
- Mucin positive
- Microcystic
- Well differentiated papillary
- Signet ring
Treatment and Prognosis of Epithelial Mesothelioma
Treatment typically depends on the type and stage of mesothelioma, but the epithelial cell type of the disease tends to have the most favorable prognosis.
Because epithelial cells tend to respond better to mesothelioma treatment, patients with this cell type may be eligible for a more aggressive treatment plan.
This may include some combination of chemotherapy, radiation therapy and surgery in an approach called multimodal therapy.
Consulting with an experienced mesothelioma care team is the best way to ensure you receive the most appropriate treatment for your cancer.
This group can accurately determine your pleural mesothelioma cell type and develop a specialized treatment plan for you.



