Mesothelioma Cancer
Malignant mesothelioma is a type of cancer caused by asbestos exposure. Tumors form on the mesothelial lining of the lungs, abdomen, heart or testes. Symptoms include difficulty breathing, chest pain or abdominal pain. If diagnosed early, life expectancy improves from about one year to several years or more.
What Is Mesothelioma?
Mesothelioma is a relatively rare terminal cancer caused by asbestos exposure. Approximately 6% to 10% of people who worked regularly with asbestos products for years develop it 20 to 50 years after exposure began.
Malignant mesothelioma forms in the mesothelium, which is a protective layer of tissue lining organs in the chest, abdomen and pelvis. Mesothelioma most commonly develops in the lining of the lungs, known as the pleura. The second-most common type develops in the peritoneum, which lines the abdomen. The other two types are extremely rare and develop in the pericardium, which lines the heart, and the tunica vaginalis, which lines the testes.
Treatment for mesothelioma extends survival from an average of six months without treatment to 12 months with treatment. Patients diagnosed at an early stage of development who undergo aggressive treatment may live three to five years or longer. Statistics for mesothelioma show the five-year survival rate is 10% for all types of mesothelioma cancer.
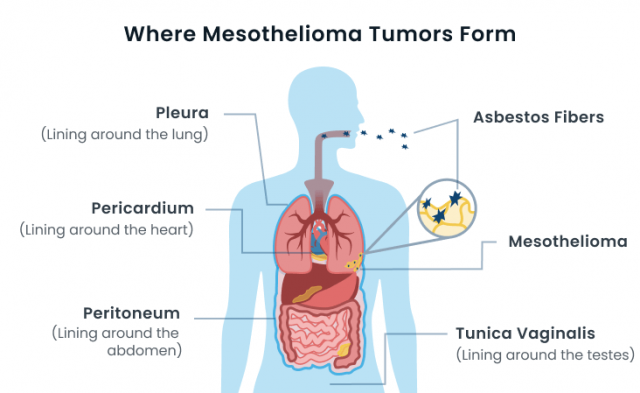
What Causes Mesothelioma?
Asbestos exposure causes nearly all cases of mesothelioma. The heavier the asbestos exposure and the longer a person is exposed throughout their lifetime, the higher the risk of mesothelioma.
Asbestos is responsible for about 80% to 90% of all mesothelioma cases. Most of this contact with asbestos has occurred in occupational settings.
Additional risk factors include exposure to asbestos while serving in the U.S. military, living with an asbestos worker or living near as asbestos mine. U.S. military veterans are at risk of developing mesothelioma because the armed forces used asbestos on ships, automobiles and planes, and in shipyards, military bases and barracks.
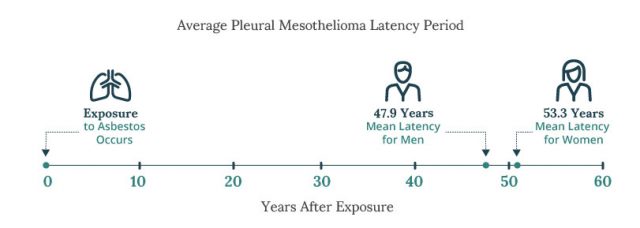
There is a long latency period associated with mesothelioma and asbestos exposure. Most mesothelioma cases start to develop about 20 to 50 years after the exposure began. This latency period can make it difficult for patients to recall when and how they were exposed to asbestos.

What Are the Symptoms of Mesothelioma?
Symptoms of mesothelioma usually do not appear until stage 3 or stage 4 of the cancer’s progression.
- Shortness of breath
- Chest pain
- Wheezing
- Coughing
- Fluid around the lungs or abdomen
- Fatigue
- Weight loss
- Fever or night sweats
- Trouble swallowing
- Changes in bowel habits
- Abdominal pain and swelling
It’s important for anyone with a history of asbestos exposure to learn as much as they can about when, where and how they were exposed. It is vital to share this information with your primary care doctor and specialists if you develop symptoms because it will help them test for asbestos-related diseases.
Common Mesothelioma Symptoms
The most common early symptoms of pleural mesothelioma include difficulty breathing and chest pain. Abdominal pain and swelling are the most common initial symptoms of peritoneal mesothelioma.
| Pleural Mesothelioma | Peritoneal Mesothelioma |
|---|---|
| Shortness of breath | Abdominal pain |
| Chest pain | Abdominal swelling |
| Wheezing | Changes in bowel habits |
| Coughing | Fluid around the abdomen |
| Fluid around the lungs | Weight loss |
| Trouble swallowing | Diarrhea or constipation |
Both pleural and peritoneal mesothelioma patients experience fatigue, weight loss, fever and night sweats. As the cancers progress, patients may experience nerve pain, back pain and loss of appetite.
Types of Mesothelioma
There are four types of mesothelioma:
- Pleural mesothelioma forms in the lining of the lungs.
- Peritoneal mesothelioma develops in the lining of the abdomen.
- Pericardial mesothelioma forms in the lining of the heart.
- Testicular mesothelioma develops in the lining of the testicles.
Pleural and peritoneal mesothelioma are the two most common types and account for 98% of all cases. The pericardial and testicular types are extremely rare and each account for approximately 1% of cases. There are also three cell types that make up mesothelioma tumors: Epithelial, biphasic and sarcomatoid.
Patients with peritoneal mesothelioma have a better chance of long-term survival with aggressive treatment than pleural mesothelioma patients. Pericardial and testicular mesothelioma are so rare that survival data is mixed. Pericardial patients live about six to 10 months and testicular patients may live for years if they have successful surgery.
Pleural Mesothelioma
Pleural mesothelioma is the most common form the disease, accounting for more than 75% of cases. Patients are typically diagnosed at a late stage of cancer development because the disease doesn’t cause symptoms until stage 3 or stage 4.
The prognosis for pleural mesothelioma is poor. Life expectancy is around one year with chemotherapy and 22 months with a combination of surgery, chemotherapy and radiation.
Peritoneal Mesothelioma
Peritoneal mesothelioma develops in the abdominal lining and accounts for approximately 20% of cases. The prognosis is around one year with chemotherapy.
About one-fifth of peritoneal patients are diagnosed early enough to qualify for cytoreductive surgery with heated chemotherapy, which helps half of the patients who receive it live longer than five years.
Pericardial Mesothelioma
Pericardial mesothelioma develops in the lining of the heart and makes up less than 1% of all mesothelioma cases. It is treated with chemotherapy and surgery.
Average survival is six to 10 months with treatment, but some patients have lived for years following successful surgery.
Testicular Mesothelioma
Testicular mesothelioma develops in the lining of the testes and also makes up less than 1% of all mesothelioma cases. Treatment involves surgery, chemotherapy and sometimes radiation.
Almost half of patients survive five years after diagnosis, and just over a third survive 10 years, according to a 2019 study published in the journal Urology.
Mesothelioma Cell Types
Mesothelioma tumors are made up of cells that pathologists have classified based on their appearance, structure, behavior and response to treatment. Epithelial cells respond the best to treatment, which means they are associated with longer survival.
Sarcomatoid cells are associated with fast tumor spread and poor response to treatment, which means they are associated with the shortest survival time. Biphasic mesothelioma is made up of both epithelial and sarcomatoid cells. Response to treatment and survival depends on the ratio of cells.
- Epithelioid Mesothelioma
-
Epithelial mesothelioma, also called epithelioid mesothelioma, is less aggressive than other cell types. It typically has a more positive prognosis compared with sarcomatoid and biphasic tumors.
- Sarcomatoid Mesothelioma
-
The sarcomatoid mesothelioma cell type is the least common form of the disease. Up to 20% of pleural mesothelioma diagnoses are of the sarcomatoid tumor type. These cells are aggressive and more difficult to treat.
- Biphasic Mesothelioma
-
Biphasic mesothelioma is a mixture of epithelial and sarcomatoid cells. To be classified as a mixed cancer, the tumor must contain at least 10% of each type of cell.
How Mesothelioma Is Diagnosed
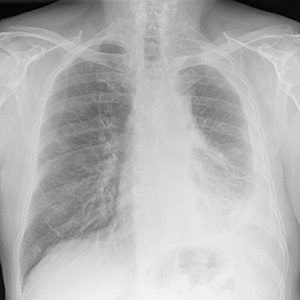
The diagnostic process begins when a patient goes to the doctor and describes their symptoms and asbestos exposure history. It is important to share everything you know about how and where you were exposed so doctors know to test for asbestos-related diseases.
Diagnosing mesothelioma is a complex process that involves biopsies to confirm what type of cancer cells are present. Imaging scans help determine the stage of the cancer.
Testing for mesothelioma may involve the following procedures:
- Biopsies: A thoracoscopic biopsy is the most accurate test to confirm a mesothelioma diagnosis. Other biopsies may be used such as fine-needle aspiration, thoracentesis or mediastinoscopy.
- Blood Tests: While blood tests are not used to confirm a mesothelioma diagnosis, they are helpful in determining a patient’s overall health and response to treatment.
- Imaging Scans: X-rays, CT scans, PET scans and MRIs may be used to identify where tumors are located.
Mesothelioma specialists are at the forefront of treatment for this rare cancer and remain a patient’s best chance of living longer with the disease. They can provide a second opinion that may give a more accurate diagnosis and can offer more innovative treatment options.
Misdiagnosis is relatively common for mesothelioma because the initial symptoms may appear mild or indicative of a less serious condition. Patients may be misdiagnosed with pneumonia, chronic bronchitis, lung cancer or inflammatory bowel disease before receiving the correct diagnosis.
Stages of Mesothelioma Cancer
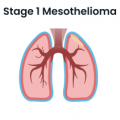
- Stage 1 Mesothelioma
-
Mesothelioma cancer cells remain within the pleural lining.
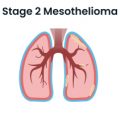
- Stage 2 Mesothelioma
-
Cancer cells have spread into lung tissue and nearby lymph nodes.
- Stage 3 Mesothelioma
-
Cancer cells have spread into neighboring tissue such as the chest wall.
- Stage 4 Mesothelioma
-
Spreading of cancer cells continues throughout the chest cavity on both sides. In some cases, cancer cells spread into the abdominal lining or distant organs.
The staging of mesothelioma is an important part of the diagnostic process because it guides treatment recommendations. For example, early-stage patients often qualify for surgery because the tumors are easier to remove.
Only pleural mesothelioma has official staging systems. A staging system is in development for peritoneal mesothelioma, but more data is required to make it official.
Two systems are used to stage pleural mesothelioma: TNM and SEER. TNM has four stages and measures cancer growth by tumor size, lymph node involvement and whether the cancer has metastasized. SEER has three stages defined by cancer spreading at local, regional and distant locations.
What Is the Life Expectancy of Mesothelioma?
Your life expectancy, or how long you may live with mesothelioma, is based on survival rate statistics compiled from data on people who had mesothelioma in the recent past. The term prognosis refers to the impact the disease will have on your overall health.
Most patients who undergo chemotherapy have a life expectancy of one year. The five-year survival rate is around 10% for all types of mesothelioma. The prognosis for mesothelioma is poor because there is no cure for this terminal disease. However, some mesothelioma survivors have lived a long time despite the poor prognosis.
Survival is different among pleural and peritoneal patients who qualify for surgery. Surgical pleural patients live an average of 22 months. Surgical peritoneal patients have a 50% chance of living longer than five years.
The biggest factors that impact prognosis include stage at diagnosis and treatment. Early-stage patients respond best to treatment and tend to live longer. Women tend to live longer than men, and a younger age also improves chances of longer survival.
Mesothelioma Survivors
Many mesothelioma survivors credit the doctors who oversaw their treatment and the people who supported them along the journey as vital to their survival.
Joanne D. was diagnosed with pleural mesothelioma in 2009 and underwent a pleurectomy and decortication surgery by the late Dr. David Sugarbaker. She has since had two recurrences of cancer that were treated successfully with surgery and chemotherapy.
Sydney R. was diagnosed with pleural mesothelioma in 2011 and was given about a year to live. She sought second and third opinions to find more treatment options. She successfully underwent a pleurodesis, multiple rounds of chemotherapy and radiation, a pleurectomy and a pneumonectomy.
Kathleen A. was diagnosed with pleural mesothelioma in 2010 and did not like the diagnosis and prognosis she was given, so she also sought second and third opinions. She decided on aggressive treatment with a pleurectomy and decortication surgery by Dr. Tracey Weigel at the Carbone Cancer Center in Madison, Wisconsin.

Mesothelioma Treatment
The mesothelioma treatment options your doctor recommends will depend upon the location of the cancer, the stage of progression, the tumor cell type and the patient’s overall health.
Because mesothelioma is so difficult to diagnose and treat, it is vital to see a mesothelioma doctor who specializes in either pleural or peritoneal mesothelioma.
A mesothelioma specialist has the expertise to develop the best treatment plan for you, and they work at cancer centers where the latest clinical trials and treatments are available.
Some patients who are diagnosed early qualify for a combination of surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy. This is known as multimodal treatment.
Surgery
The two aggressive surgeries used to remove pleural mesothelioma tumors are pleurectomy and decortication, or P/D surgery, and extrapleural pneumonectomy, or EPP surgery. The P/D surgery spares the lung, while the EPP surgery removes the cancerous lung. Both surgeries remove the pleural lining and any visible cancerous tissue.
Cytoreductive surgery attempts to remove all visible peritoneal mesothelioma tumors before the abdomen is washed in a heated chemotherapy bath. Half of all patients who receive the procedure live at least five years.
Chemotherapy
The most common treatment for all types of mesothelioma is chemotherapy. Chemotherapy drugs used to treat mesothelioma include cisplatin, Alimta (pemetrexed), gemcitabine (Gemzar) and carboplatin.
Chemotherapy may be delivered systematically throughout the body or heated and applied directly to mesothelial linings. Hyperthermic intraperitoneal chemotherapy, or HIPEC, treats peritoneal mesothelioma. Hyperthermic intrathoracic chemotherapy, or HITHOC, is applied to the pleural lining.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy may be used individually to treat painful chest wall tumors in pleural mesothelioma patients, or in combination with other treatments as part of a multimodal therapy plan.
Radiation therapy is generally not used in peritoneal or pericardial mesothelioma treatment because of the damage it can cause to internal organs and the heart. It is sometimes used to treat testicular mesothelioma.
Immunotherapy
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved a new immunotherapy drug combination for the treatment of pleural mesothelioma in October 2020. The drugs are nivolumab and ipilimumab, known under the brand names Opdivo and Yervoy.
Mesothelioma patients have also taken pembrolizumab, which is marketed under the brand name Keytruda. While immunotherapy drugs work differently for each patient, some patients add a year or more to their life expectancy by undergoing immunotherapy.
TTFields
A new therapy known as Tumor Treating Fields, in combination with chemotherapy, was approved by the FDA in 2019 to treat pleural mesothelioma. TTFields uses alternating electrical fields to limit cancer growth and spreading.
The therapy is administered through insulated pads that adhere to the skin and connect to a portable device that generates the alternating electrical fields. The device can be used anywhere, and it adds an average of six months of survival time to the typical one-year survival rate.
Clinical Trials
Clinical trials are how new drugs and therapies become available to future patients. They are developed by medical researchers and overseen by the FDA to ensure safety.
While there are risks to those participating in clinical trials, such as side effects and the drug or treatment not working, many patients feel the potential benefits outweigh the risks. Benefits may include the therapy adding months or years to your life span, and the knowledge you are contributing to the development of future mesothelioma treatments.
Mesothelioma Support and Awareness
Patients and families coping with a mesothelioma diagnosis benefit from a strong system of support.
Finding resources and building a support team aren’t easy when you’re undergoing treatments or caring for a loved one with cancer. However, it is essential in reducing stress and getting your family the help they need.
Support often comes from family members, friends, loved ones, neighbors, religious organizations and local charities. They may help you with transportation to medical appointments, offer to go grocery shopping or prepare meals, or help with chores around the house.
Your support group may also help you spread awareness about mesothelioma. The disease is rare, and few people know it is caused by asbestos exposure. You can help prevent future cases of mesothelioma by raising awareness about the disease and how to prevent it.
People who develop mesothelioma may be eligible for compensation to help cover costs of treatment, travel expenses and loss of income. To learn more about this option, you should consult a qualified mesothelioma lawyer. Working with an experienced attorney is your best chance of receiving the most compensation possible.
Common Questions about Mesothelioma
- How do you get mesothelioma?
-
The primary cause of mesothelioma is exposure to asbestos. Most people with mesothelioma were exposed to asbestos products through their occupations. Once inhaled, asbestos fibers can become stuck inside lung and abdominal tissue, causing damage over 20 to 50 years before mesothelioma begins to develop.
- What are the warning signs of mesothelioma?
-
There are no unique warning signs of mesothelioma, but the most common initial symptoms include difficulty breathing and chest pain. The only way to know if you have mesothelioma is to see a mesothelioma specialist for a biopsy. A biopsy is the only test that can confirm a mesothelioma diagnosis.
- Can mesothelioma go into remission?
-
Yes, mesothelioma can go into partial or full remission. Partial remission is more common and full remission is rare. The prognosis for mesothelioma is generally poor, but it depends upon the cell type and the stage at diagnosis. The average life expectancy is around one year, with 10% living more than five years. Some patients survive longer thanks to early diagnoses and positive responses to treatment.
- Is mesothelioma treatable?
-
There are treatments to improve survival, but there is no cure for the disease yet. The most common treatments for mesothelioma include immunotherapy, chemotherapy, radiation therapy, Tumor Treating Fields and surgery. Some patients qualify for experimental therapies through clinical trials.



