What Are the Most Common Mesothelioma Treatment Options?
Undergoing treatment helps people live longer with malignant mesothelioma. The longest survival rates are seen among patients who undergo a combination of surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy.
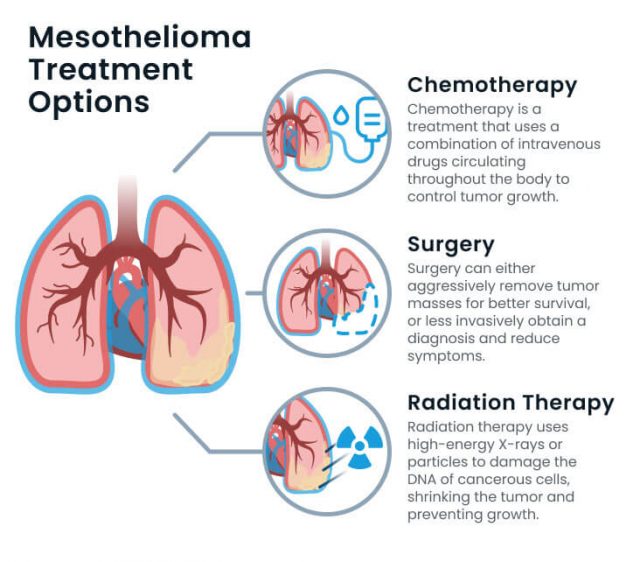
Most Common Mesothelioma Treatment Options:
- Chemotherapy
- Surgery
- Radiation therapy
This treatment approach is called multimodal therapy, and it helps some people live for years with mesothelioma. Patients must be in good health and diagnosed at an early cancer stage to be eligible.
Emerging treatment options for pleural mesothelioma such as immunotherapy, photodynamic therapy and anti-angiogenic therapy are available through clinical trials.
Surgery
Mesothelioma surgery has proven to be the best standard treatment option for long-term survival. It is also used to control symptoms.
Specialists have developed two tumor-removing surgical procedures for pleural mesothelioma. A pleurectomy and decortication spares the lung, while an extrapleural pneumonectomy completely removes the cancerous lung.
There are also two palliative surgical options that focus on treating pleural effusion, one of the most common symptoms of pleural mesothelioma. Pleural effusion is fluid that accumulates in the space around the lungs. It can make breathing painful and difficult.
Surgeons must determine whether a patient has resectable or unresectable mesothelioma to identify the best candidates for tumor-removing or palliative surgery.
- Resectable
-
The tumors can be removed with surgery. Patients with resectable mesothelioma are eligible for the more aggressive tumor-removing surgeries.
- Unresectable
-
The tumors cannot be removed with surgery. Patients with unresectable mesothelioma are eligible for palliative surgeries.

Extrapleural Pneumonectomy
An extrapleural pneumonectomy, also known as an EPP, is an extensive surgery involving the removal of the entire affected lung, the linings of the chest and heart, and the diaphragm. Though this procedure gives the surgeon a good chance of removing the tumor from the body, removing a lung also permanently impairs the patient’s stamina.
Pleurectomy and Decortication
A pleurectomy and decortication, also known as P/D, is a less radical surgery in which the surgeon removes the linings of the chest and heart, and sometimes the diaphragm, but spares the lung. This procedure has become a good option for multimodal therapy, because it provides similar benefits as an extrapleural pneumonectomy with fewer risks of complications.
Thoracentesis
A thoracentesis procedure drains the fluid from a pleural effusion, relieving the pressure on the lung.
Pleurodesis
A pleurodesis procedure drains the fluid and goes a step further by also sealing the pleural space to prevent any further fluid buildup.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy for mesothelioma is the most widely received treatment. Since most patients don’t qualify for surgery, chemotherapy is the next best option.
It involves the use of one or more drugs to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. The drugs are usually delivered into a patient’s vein through an IV.
The most commonly used chemotherapy drugs for pleural mesothelioma is a combination of cisplatin and Alimta (pemetrexed). On its own, chemotherapy can slow cancer progression, ease symptoms and prolong survival.
When combined with other therapies, chemotherapy can improve treatment results.
- Administering chemotherapy before surgery and radiation therapy can shrink the tumor, making it easier to target.
- Chemotherapy after surgery can help kill any cancer cells left in the body.
Chemotherapy drugs damage cells that divide quickly, which is what makes chemotherapy an effective cancer treatment. However, because there are also many normal cells in the body that divide quickly, chemotherapy usually has harsh side effects.
Chemotherapy Side Effects
- Fatigue
- Nausea and vomiting
- Hair loss
- Mouth sores
- Diarrhea and constipation
- Anemia (lack of blood)
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy for mesothelioma is used for specific purposes in treatment. It uses high-energy particles to damage the DNA in cancer cells, which stops them from growing and dividing.
- When used alone, it can relieve chest pain by shrinking tumors invading the chest wall.
- When used in combination with surgery, it can reduce the risk of localized recurrence.
Radiation therapy has been used to prevent tumor spreading to incisions after surgery. However, a 2019 phase III clinical trial published in the Journal of Clinical Oncology found it relatively ineffective for this purpose.
As a palliative treatment for late-stage patients, radiation can shrink tumors and significantly relieve pain.
Radiation therapy is painless during the procedure, but it can have some side effects.
Radiation Therapy Side Effects
- Fatigue
- Nausea
- Skin irritation near the application area (similar to sunburn)
Depending on the dosage and frequency of the radiation, long-term radiation damage may also occur.

Multimodal Therapy
The most effective multimodal therapy approach for mesothelioma treatment is a combination of surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy. About 20 percent of pleural mesothelioma patients qualify for this aggressive treatment plan.
Establishing a Treatment Plan
Establishing a treatment plan is a coordinated effort between mesothelioma specialists and their patients. Doctors recommend different therapies with the goal of helping patients live as long as possible.
- Surgery, chemotherapy and radiation therapy will be recommended to patients in good health with early stage cancer.
- Chemotherapy and immunotherapy may be recommended to patients who are not eligible for surgery. Immunotherapy is usually available through clinical trials or compassionate use programs.
- No survival benefit has been observed by combining chemotherapy with radiation therapy in nonsurgical patients. However, combining chemotherapy with anti-angiogenic drugs or immunotherapy drugs is showing promise in clinical trials.
It is up to each patient to decide what treatments they want to undergo. It is important to discuss all the risks and benefits with a medical professional to ensure you thoroughly understand your options.
Complementary Therapies
Complementary therapies are treatments that don’t aim to treat the cancer itself, but instead relieve cancer symptoms or treatment side effects.
Palliative Care
Palliative care, also known as supportive care, aims to control pain, relieve symptoms and improve quality of life.
Palliative care specialists use a wide variety of therapies to manage pain and symptoms.
- Medications are used to control pain and swelling, ease anxiety and promote sleep.
- Physical, occupational and respiratory therapies are used to improve a patient’s quality of life and ability to breathe.
Ask your oncologist for a referral to a palliative care specialist. This kind of care is complementary at every phase of treatment and recovery.
Alternative Therapies
Many patients turn to alternative medicine for help coping with the symptoms of pleural mesothelioma and the side effects of cancer treatments. These therapies include a diverse range of practices — with some based in the life sciences or mystical belief systems, and others falling somewhere in between.
Alternative therapies vary significantly in terms of the scientific evidence supporting them. For example, yoga, massage and nutritional therapy have proven health benefits, but energy healing techniques, such as reiki, remain a matter of faith.
Consider the following guidelines before trying alternative therapies:
- Check with your doctor before beginning any alternative therapy.
- Be skeptical of anyone who offers you a “miracle drug” as there currently is no cure for mesothelioma.
- Research alternative medicine practitioners before you decide to work with them.
- Research any herbal remedy or natural medicine using it. Make sure to read information about side effects and potential drug interactions.
If a certain practice brings you peace of mind, and your medical team has given their approval, then it may indeed help you heal in some way.
New Treatment Options
Doctors are researching and developing new treatment options for pleural mesothelioma, but they require rigorous testing to prove their effectiveness and safety before the U.S. Food and Drug Administration will approve them.
Clinical Trials
Research studies called clinical trials allow scientists and doctors to experiment with drugs and therapies in different combinations and doses, as well as test the safety and effectiveness of entirely new methods of treatment.
The ultimate goal of mesothelioma clinical trials is to find new and improved treatment strategies. Three innovative therapies under investigation include immunotherapy, photodynamic therapy and anti-angiogenic therapy.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is a type of treatment that helps the immune system fight cancer. The Food and Drug Administration has approved immunotherapy to treat several types of cancers, including lung cancer, but not mesothelioma.
Immunotherapy for mesothelioma is available through clinical trials and compassionate use programs. It is most successful when used in addition to standard treatments such as surgery and chemotherapy.
The targeted approach of immunotherapy means some patients experience fewer side effects. However, some patients develop side effects caused by kick-starting the immune system.
Immunotherapy Side Effects
- Flu-like symptoms
- Rashes
- Chronic fatigue
- Low fever
- Changes in blood pressure
Tumor Treating Fields (TTFields)
In May 2019, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration approved Tumor Treating Fields as a new pleural mesothelioma treatment. TTFields uses alternating electrical currents to disrupt cancer cell growth and shrink tumors.
Doctors prescribe TTFields alongside pemetrexed (Alimta) and platinum-based chemotherapy for patients who are ineligible for surgery. The treatment is painless, and patients carry a portable battery device that delivers TTFields treatment through adhesive patches worn throughout the day.
Photodynamic Therapy
Photodynamic therapy uses a light-activated drug called a photosensitizer to kill cancer cells.
The most common photosensitizer used to treat pleural mesothelioma is porfimer sodium, more commonly known as Photofrin. The drug is usually injected into a vein, allowing it to spread throughout the body’s cells.
It remains in cancerous cells longer than in healthy cells, and treatment begins two or three days after the drug has left most of the healthy cells. This therapy is primarily available through clinical trials, although some mesothelioma surgeons are known to use it outside a trial setting.
Because it does not target healthy cells, this pleural mesothelioma treatment has fewer side effects than standard chemotherapy.
Anti-Angiogenic Therapy
Anti-angiogenic drugs prevent tumors from forming new blood vessels, which allow cancer cells to spread to new locations. These drugs work by preventing tumors from spreading, a process known as metastasis.
- French researchers developed a drug called Avastin (bevacizumab), and it has become part of first-line standard of care in France for pleural mesothelioma.
- German researchers are developing a drug called nintedanib, also known by the brand names Ofev and Vargetef, which they say is even more effective than Avastin.
Anti-angiogenic drugs are typically given in combination with chemotherapy. These drugs are known to increase the side effects patients experience, but under the right medical supervision the side effects are manageable.

Recurring Mesothelioma
Mesothelioma treatment can put the cancer into partial remission, which means tumors either shrink or stop growing. Unfortunately, the cancer usually returns, and this is called a mesothelioma recurrence.
Top Second-Line Therapies for Treating Recurring Mesothelioma:
- The most common is chemotherapy. Different drugs are used the second time around.
- Some patients undergo a second surgery, but this is more common in the peritoneal form of the disease than in pleural mesothelioma. Some patients also undergo another round of chemotherapy after their second surgery.
- Sometimes radiation therapy is used to treat a painful recurrence that grows into the chest wall.
How patients respond to second line treatment depends on a number of factors such as their age, overall health and how fast their tumors are growing.
Mesothelioma Specialists and Treatment Centers
It is important to work with a mesothelioma doctor to access the best treatment. These specialists are located at cancer centers featuring the most innovative approaches to treating mesothelioma.
A pleural mesothelioma patient’s best hope of improving their prognosis is to seek a team of medical professionals with experience treating the disease.
There are several specialized mesothelioma cancer centers spread across the United States with expert staff dedicated to developing the best treatments for patients.
What Is the Cost of Mesothelioma Treatment?
A patient’s treatment options will depend on the specifics of their diagnosis, and their out-of-pocket expenses for mesothelioma treatment will depend on their health insurance coverage.
Average Costs of Mesothelioma Treatment Options
- Radiation therapy may cost around $2,000 a month.
- The cost of chemotherapy may exceed $10,000 a month.
- The average cost of a major thoracic cancer surgery is around $40,000.
Forms of Mesothelioma Financial Assistance:
- Grants for travel, housing and treatment are available to help patients take advantage of top cancer centers.
- Because almost all mesothelioma cases are caused by asbestos, many former asbestos companies established trust funds to compensate victims of exposure.
- Compensation is also available through mesothelioma lawsuits, Social Security Disability Insurance and VA benefits.




